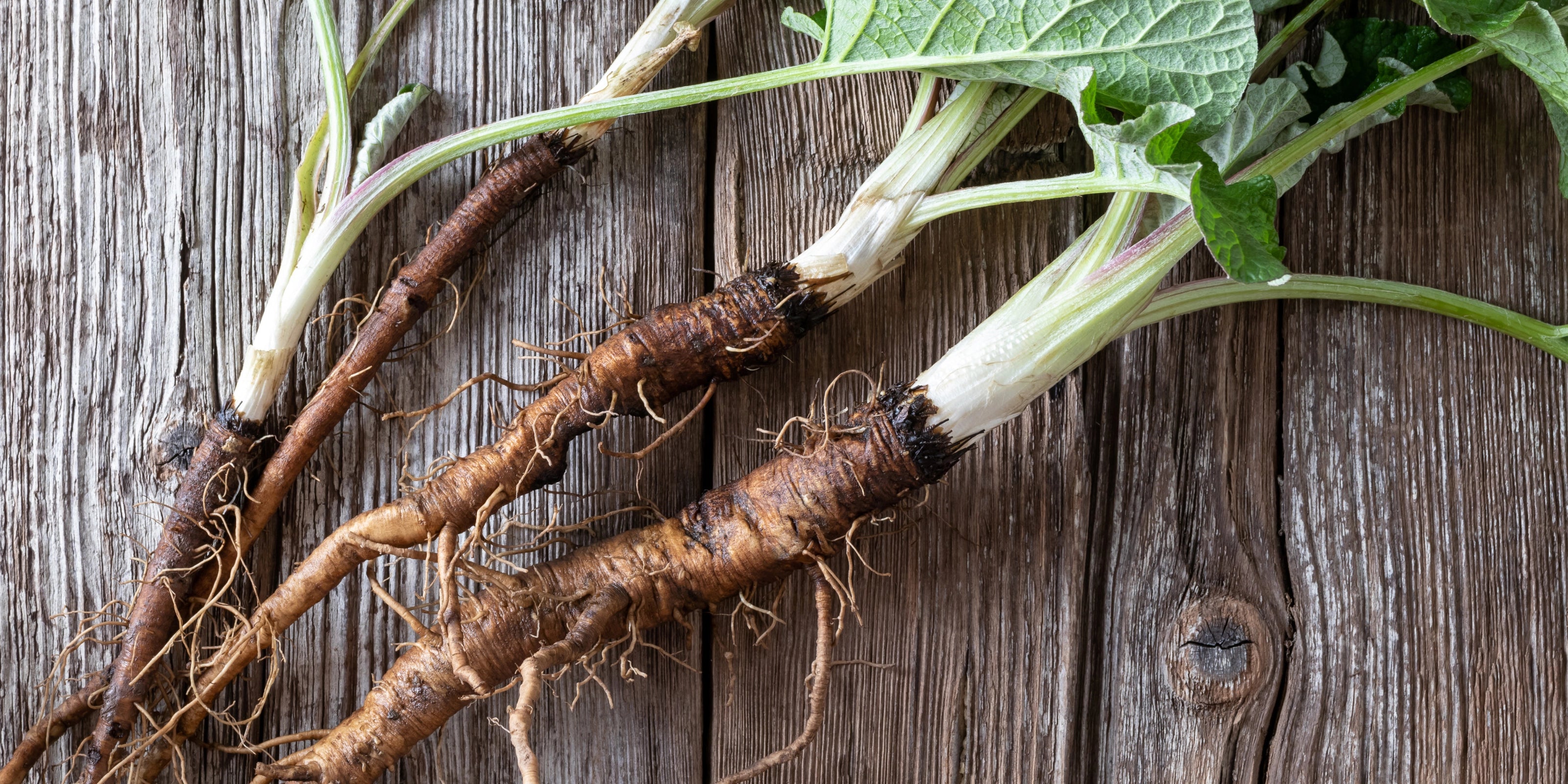
Burdock root, known scientifically as Arctium lappa, is a vegetable native to Northern Asia and Europe, though it now grows in the United States. The burdock plant’s deep roots are very long and vary in color from beige to brown and nearly black on the outside. Burdock root has been used for centuries in holistic medicine to treat a variety of different conditions. Traditionally, it’s been most commonly used to treat infections and wounds. This blog post delves into what burdock is, its historical significance, and why it continues to be a staple in herbal medicine cabinets around the world.
Historical Uses of Burdock
Historically, burdock has been used across continents for centuries. In Europe, it was a familiar staple in traditional herbal medicine, often used to treat a variety of ailments from skin conditions to fever and joint pain. In Asia, particularly in Japan, it is known as "gobo" and is still commonly used as a food ingredient in dishes like kinpira gobo, where it is sautéed with soy sauce, sugar, and mirin.
Burdock’s use in Native American medicine also included treatments for ailments such as colds and even as a diuretic or blood purifying agent. The breadth of its applications speaks volumes about its perceived efficacy across different cultures and generations.
Nutritional Profile
Burdock root is rich in several vital nutrients. It is an excellent source of dietary fiber, vitamin B6, magnesium, and potassium. Its fiber content makes it beneficial for digestive health, while the presence of antioxidants helps combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
Health Benefits of Burdock
-
Skin Health: Historically, burdock root has been utilized for treating various skin issues due to its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial qualities, which may help prevent skin infections and enhance skin recovery. A small study indicated that individuals with acne who consumed burdock root supplements orally experienced a reduction in pimples and an improvement in quality of life over six months. However, the study lacked a control group, which limits the conclusiveness of the results.
-
Digestive Support: The inulin content, a type of soluble fiber in burdock root, aids in digestion and maintaining a healthy gut by promoting beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. Inulin supports digestion by boosting the population of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. These bacteria are important for defending against harmful pathogens (bad bacteria), preventing infections and enhancing the immune system. Additionally, inulin increases the bulk of your stool and the frequency of your bowel movements. While you may experience more frequent bowel movements, inulin actually slows down the overall digestion process, allowing your body to absorb more nutrients from the food you consume. Research also indicates that inulin may improve the body's ability to absorb calcium, which is essential for building a stronger skeletal system.
-
Detoxification: Studies on traditional medicine show that burdock root contains active compounds that can help remove heavy metals from the blood, enhancing the health of organs and the overall body.
-
Antioxidant Powerhouse: The root is loaded with antioxidants, such as quercetin, luteolin, and phenolic acids, which help protect cells from damage and decrease inflammation.
Adding Burdock to Your Diet
Burdock root can be consumed in various ways. It can be eaten raw, cooked, or as a supplement form. As always, consult with a healthcare provider before adding new herbal supplements to your routine, especially if you have existing health conditions or are on medication.
Conclusion
Burdock root is not just a simple weed, but a versatile and potent plant with a rich history in traditional medicine. Whether used for its nutritional benefits, detoxifying properties, or skin health capabilities, burdock makes an excellent addition to a holistic health regimen.